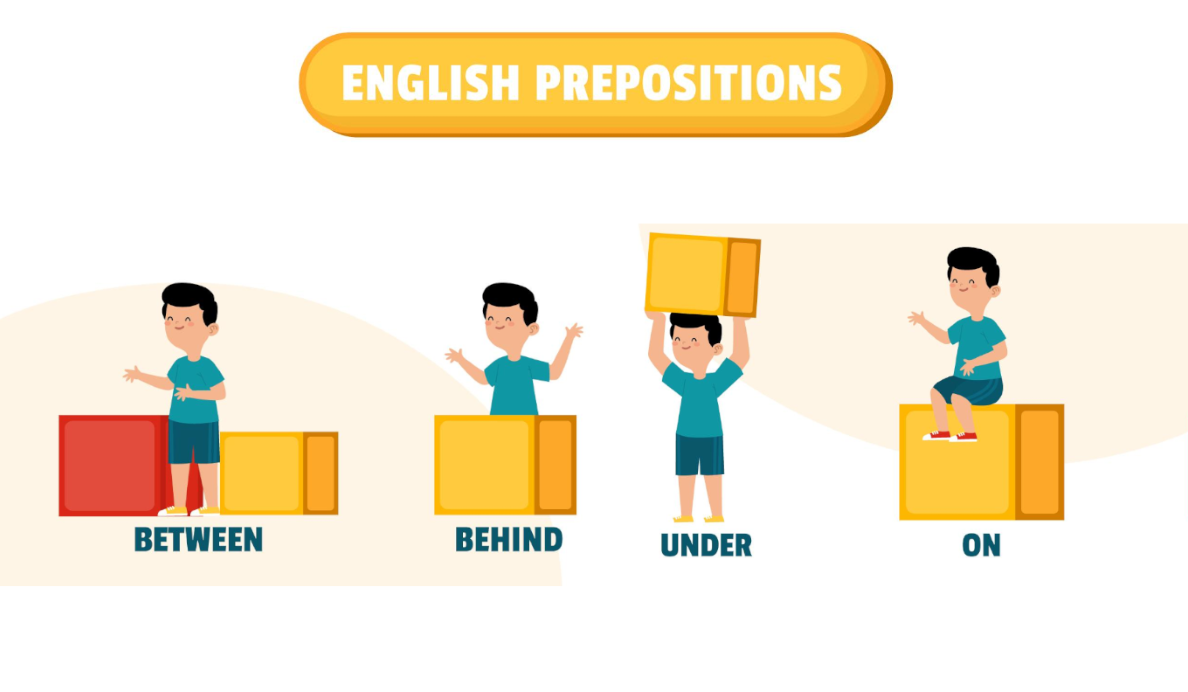
Expressing position
When expressing position, we use prepositions to indicate the location of an object or person.
For example, "The book is on the table" or "The cat is under the chair." Common prepositions of position include "on," "under," "in," "beside," "behind," and "next to." These prepositions help us describe where something or someone is located.
Rules for expressing position
👉 Prepositions of position: Prepositions such as "on," "under," "in," "beside," "behind," and "next to" are used to describe the location or position of an object or person.
👉 Nouns and pronouns: The position of an object or person is often described in relation to a noun or pronoun. For example, "The book is on the table," or "She is standing next to me."
👉 Word order: In English, the usual word order for expressing position is "preposition + noun/pronoun." For example, "in the box," "under the chair," or "beside the tree."
Uses of expressing position
- 👉 Describing location: Expressing position helps us provide information about where something or someone is located.
For example, "The keys are on the kitchen counter," or "The park is near my house."
- 👉 Giving directions: When asking for or giving directions, expressing position is essential. It helps us understand the relative location of places and navigate our surroundings.
For example, "Turn left at the traffic lights," or "Go straight ahead until you see the post office."
- 👉 Identifying relationships: Expressing position helps us establish the relationships between objects or people. For instance, "The cat is hiding behind the couch," or "The bookstore is next to the café."
- 👉 Providing context: By expressing position, we provide important context to our descriptions or narratives. It helps the listener or reader visualize the scene more accurately. For example, "She was sitting on a bench in the park," or "The painting hangs on the wall in the living room."
Remember to use the appropriate preposition based on the specific location or position you want to describe. Practice using prepositions of position with different nouns or pronouns to reinforce your understanding of expressing position in English.
Emphasizing the result of an action
When we want to highlight the outcome or result of an action, we can use certain words or phrases.For instance, instead of saying "I finished the project," we can say "I successfully completed the project." This adds emphasis to the fact that the action was accomplished successfully. Other words and phrases that can be used to emphasize the result include "successfully," "effectively," "completely," and "with great success."
Rules for emphasizing the result of an action
| 🔊 | Vocabulary choice:
To emphasize the result of an action, it's important to choose appropriate words or phrases that convey the desired level of impact or success.
Consider using words such as "successfully," "effectively," "completely," "exceptionally," "remarkably," or "with great success."
|
| 🔊 | Adverbs and adjectives:
Adverbs and adjectives play a crucial role in emphasizing the result of an action.
By selecting strong and descriptive words, you can highlight the outcome more effectively.
For example, instead of saying "I finished the project," you can say "I successfully completed the project."
|
| 🔊 | Sentence structure:
Sentence structure can also contribute to emphasizing the result.
Consider placing the word or phrase that emphasizes the result at the beginning or end of the sentence for added impact.
For example, "With great determination, I achieved my goal" or "I achieved my goal with great determination." |
Asking for directions
When you're in a new place and need to find your way around, it's important to know how to ask for directions. You can start by using phrases like "Excuse me" or "Could you please tell me" to be polite. Then, you can ask questions such as "Can you tell me how to get to the nearest train station?" or "Which way is the museum?" It's also useful to know common directional vocabulary like "left," "right," "straight," "ahead," "around the corner," and "opposite."
| 🔊 | Navigating in unfamiliar places:
Asking for directions is essential when you're in a new or
unfamiliar place and need guidance to find your destination. |
| 🔊 | Locating specific places:
When you're looking for a specific location such as a restaurant, hotel,
or tourist attraction, asking for directions helps you find your way. |
| 🔊 | Getting information about routes:
If you're unsure about the best route to take or need information
about transportation options, asking for directions can provide you with valuable information. |
| 🔊 | Clarifying directions:
Sometimes, the initial directions may be unclear or confusing.
Asking for clarification helps ensure that you
understand the directions accurately. |
Example questions for asking directions:
| 🔊 | Excuse me, could you please tell me how to get to the nearest train station? |
| 🔊 | Which way is the museum? |
| 🔊 | Can you tell me how to get to Central Park? |
| 🔊 | Where can I find the nearest bus stop? |
| 🔊 | How do I get to the city center from here? |
Remember to thank the person for their help after receiving directions. Additionally, it's useful to familiarize yourself with common directional vocabulary such as "left," "right," "straight," "ahead," "around the corner," "opposite," and "near."
Using prepositions of place
Rules for using prepositions of place:
- 👉 Prepositions of place: Prepositions of place are used to indicate the position or location of something or someone in relation to other objects or people. Common prepositions of place include "in," "on," "at," "under," "over," "above," "below," "beside," "behind," and "in front of."
- 👉 Object or person + preposition: Prepositions of place are typically used after a noun or pronoun to describe its location.
| 🔊 | The book is on the table |
| 🔊 | She is standing beside me. |
- 👉 Noun or pronoun + verb + preposition: In some cases, prepositions of place can be used after a verb to indicate the direction or location of the action.
| 🔊 | He walked up the stairs |
| 🔊 | She looked under the bed. |
Uses of prepositions of place:
- 👉 Describing location: Prepositions of place help us accurately describe where something or someone is located.
| 🔊 | The cat is on the roof |
| 🔊 | The pen is in the drawer. |
- 👉 Expressing relationships: Prepositions of place also establish relationships between objects or people. They indicate proximity, distance, or relative positions.
- For instance,
| 🔊 | The school is next to the park |
| 🔊 | The car is behind the building. |
- 👉 Giving directions: Prepositions of place are essential when giving or receiving directions. They help communicate the spatial relationships between landmarks or destinations.
| 🔊 | Turn left at the intersection |
| 🔊 | Go straight ahead until you reach the bridge. |
- 👉 Spatial descriptions: Prepositions of place are used to provide spatial descriptions in various contexts. This can include describing the arrangement of objects, the layout of a room, or the location of landmarks.
- For instance,
| 🔊 | The book is on the shelf |
| 🔊 | The café is across the street. |
The passive voice
In English, we can use the passive voice to emphasize the action being done to the subject, rather than the subject performing the action. For example, instead of saying "John ate the cake," we can say "The cake was eaten by John." The passive voice is formed using the auxiliary verb "be" followed by the past participle of the main verb. It's particularly useful when the doer of the action is unknown, unimportant, or when we want to shift the focus of the sentence.
Rules for the passive voice
- Forming the passive voice: The passive voice is formed by using the auxiliary verb "be" followed by the past participle of the main verb. The form of "be" depends on the tense of the sentence (e.g., "is," "was," "will be," etc.).
| 🔊 | The cake is eaten by John |
| 🔊 | The report was written by Sarah. |
- Object becomes the subject: In the passive voice, the object of an active sentence becomes the subject of the passive sentence. The subject of the active sentence is either omitted or placed after the verb "be."
| 🔊 | They built the house" (active) becomes "The house was built" (passive) |
- Agent (optional): The agent, which is the "doer" of the action, can be included in a passive sentence using the preposition "by." However, the agent is not always necessary, especially when it is unknown or not important.
| 🔊 | "The book was written by Mark" or simply "The book was written." |
Take a look at the passive voice in several verbal tenses:
Simple Present Tense:
Active Voice: The subject performs the action.
| 🔊 | The cat chases the mouse. |
Passive Voice: The subject receives the action.
| 🔊 | The mouse is chased by the cat. |
Simple Past Tense:
Active Voice: The subject performed the action.
Passive Voice: The subject received the action.
| 🔊 | A letter was written by her. |
Present Continuous Tense:
Active Voice: The subject is currently performing the action.
| 🔊 | They are painting the walls. |
Passive Voice: The subject is currently receiving the action.
| 🔊 | The walls are being painted by them. |
Past Continuous Tense:
Active Voice: The subject was in the process of performing the action.
Passive Voice: The subject was in the process of receiving the action.
| 🔊 | Dinner was being cooked by him. |
Present Perfect Tense:
Active Voice: The subject has completed the action.
| 🔊 | We have finished our homework. |
Passive Voice: The subject has received the action.
| 🔊 | Our homework has been finished by us. |